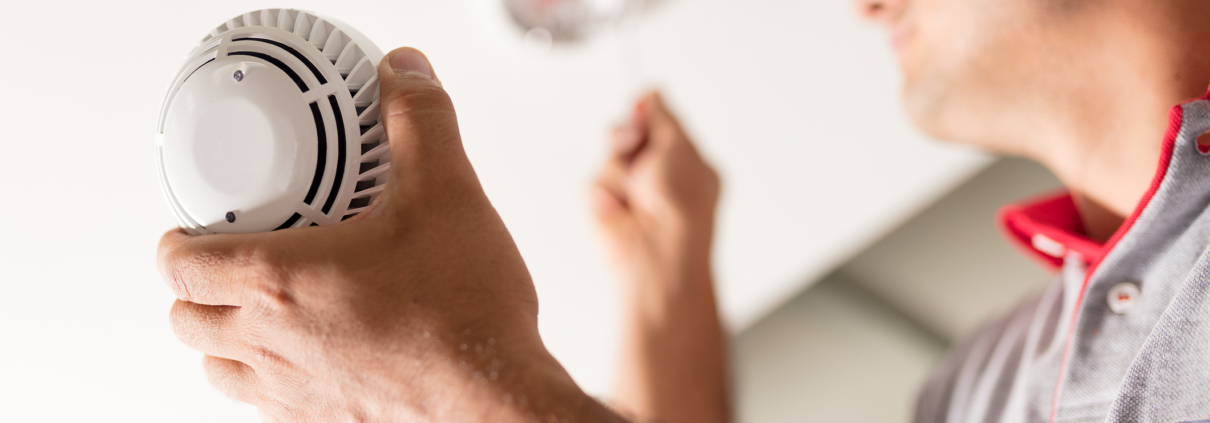
We get it, you’re working with a tight budget and didn’t consider fire safety as a part of the bottom line. While each commercial building might have different needs and pricing, investing in a clean agent fire suppression system is cheaper than the financial consequences of your building burning down.
Fire Suppression Systems
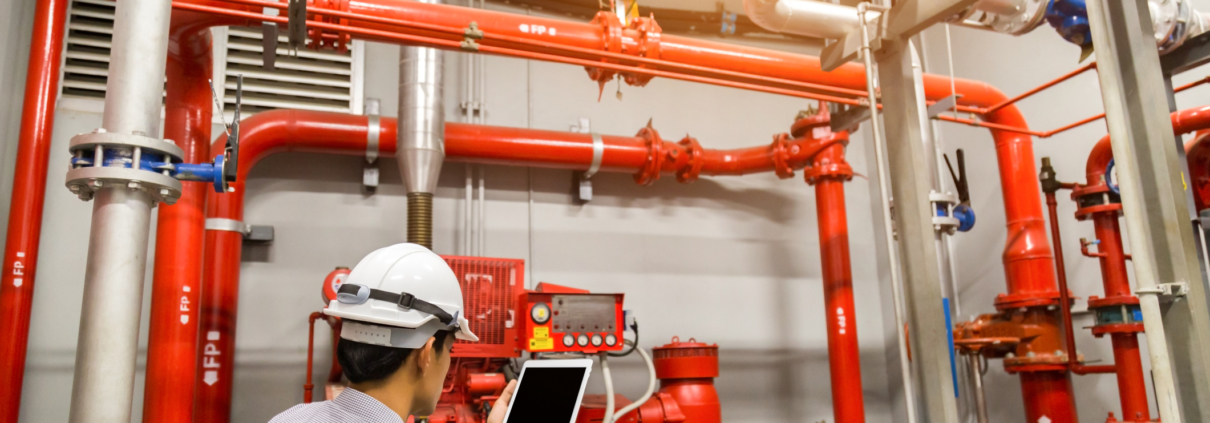
Fire suppression systems are used to extinguish or control fires and are activated by heat, smoke, or a combination of the two. Suppression systems are typically found in places like museums, libraries, data centers, and archives.
Unlike wet-pipe sprinkler systems, suppression systems use gaseous, chemical or foam agents to suppress the fire, rather than water. This aids in the preservation of sensitive equipment and content within a particular environment. There are many different applications of fire suppression depending on the area in which these systems are housed.
There are different types of fire suppression systems that VFS can install.
Clean Agent Fire Suppression
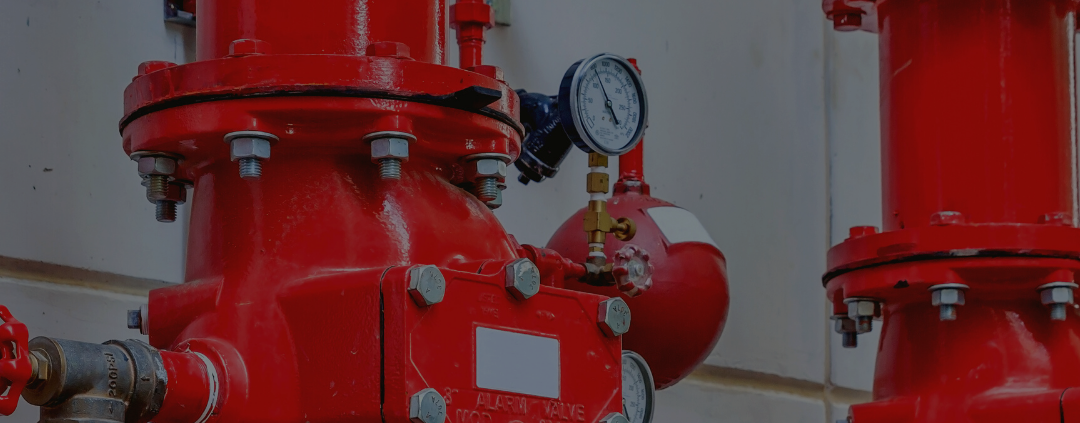
Clean agent fire suppression is a term used to describe the use of inert gases to extinguish a fire. These systems all have three main components:
- Smoke Detector
- Control Panel
- Notification Devices
When the smoke detector is triggered, it sends a signal to the control panel which then alerts the notification devices, activating the release device to suppress the fire.
Clean agent fire suppression systems are fast-acting and most effective in protecting sensitive equipment and environments because they are designed to suppress the fire in its incipient stage. Clean fire agents are electronically nonconducting and unlike water, they won’t ruin electrical components or electronics.
Clean agent fire suppression systems are most often found in server rooms, record/file repositories, and data centers that require an increased level of protection to prevent unnecessary and accidental discharge of systems.
The Details
- Inert gases: Nitrogen, argon, and carbon dioxide work together by lowering oxygen content in a room below the level that supports combustion, while still allowing a person to breathe keeping your environment and your personnel safe.
- Fluorocarbon-based extinguishers are described as “clean agents” as they do not leave any oily residues, particulates, or water damage and rapidly extinguish fires with a superb weight to effectiveness ratio. These extinguishing agents are also safe to use in occupied spaces and offer unique advantages in speed, performance, and safety.
Fun stuff, right?
There is a range of costs and options available when it comes to clean agent fire suppression systems. Contact VFS Fire & Security Services today to learn more!